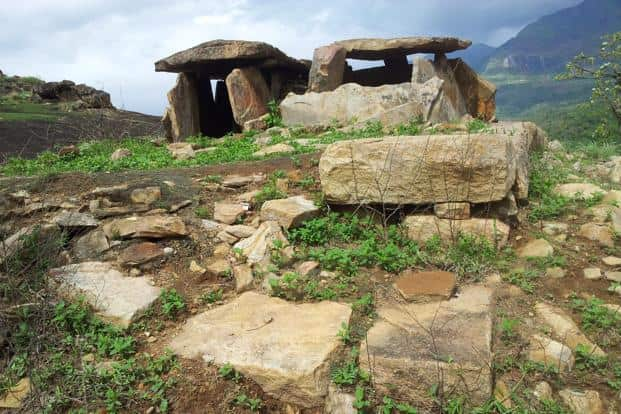

Rock art >>
Archaeological evidence
The existence of a unique, preAryan populace with a distinct cultural heritage and evolved literary traits has been fortified by archaeological evidence collected from the discovery of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro in the early 1920s, and further substantiated by the ongoing Keezhadi excavations in Tamil Nadu. With modern day advancements in handling fragile biodegradable material from excavation sites and also high-throughput genomic sequencing, we now understand how the Indian subcontinent was populated through waves of migration.
These studies confirm the historical facts that have seeped into common understanding in Tamil Nadu over the course of the century-old Dravidian Movement. In 2018, the paper titled ‘The Genomic Formation of South and Central Asia’ (co-authored by 92 scientists across a range of disciplines), further confirmed that Aryan migration into the subcontinent between 2000 BCE and 1000 BCE. Published scientific work that followed also established that the Harappans of the Indus Valley Civilisation created an agricultural revolution in the subcontinent and narrowed the period of Aryan migration to 2000 BCE and 1500 BCE.
A theory debunked
Recent scientific findings have conclusively debunked the ‘Out of India Theory’, which is part of the larger narrative suggesting that Dravidians and Aryans are ethnically similar but geographically divided. This has posed serious problems to the supporters of Golwalkar who have recently set out to discover the lost, mystic river Saraswati and to repackage the Indus Valley Civilization as the ‘Saraswati Civilization’ without taking into account research which suggests that the language of Harappans could have been Dravidian/ Proto-Dravidian. As such, C.N. Annadurai (Anna), a stalwart of the Dravidian Movement and a former Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu, had anticipated such baseless positioning in his book, Arya Mayai (Aryan Illusion). […]
Source: “The Dravidian movement and Aryan illusions” by Manuraj Shunmugasundaram, The Hindu, 23 July 2022
URL: https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/the-dravidian-movement-and-aryan-illusions/article65672119.ece
Date Visited: 25 July 2022
“We shall first have to give up this hubris of considering tribes backward. Every tribe has a rich and living cultural tradition and we must respect them.” – Vice President M. Venkaiah Naidu on the constitutional obligation to respect the cultural traditions of India’s tribal communities
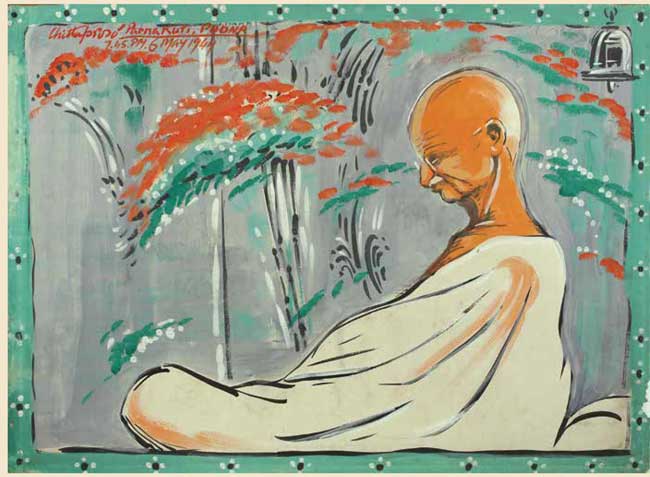

Gandhian social movement | Constitution | Adverse inclusion >>
“Air is free to all but if it is polluted it harms our health… Next comes water… From now on we must take up the effort to secure water. Councillors are servants of the people and we have a right to question them.” – Mohandas K. Gandhi, Ahmedabad address on 1 January 1918; quoted by his grandson, Gopalkrishna Gandhi, in “On another New Year’s Day: Mahatma Gandhi’s ‘khorak’ a 100 years ago” (The Hindu, 1 January 2018)
“The world has enough for everyone’s need but not for anyone’s greed.” – Mahatma Gandhi quoted by Medha Patkar and Baba Amte (Narmada Bachao Andolan)
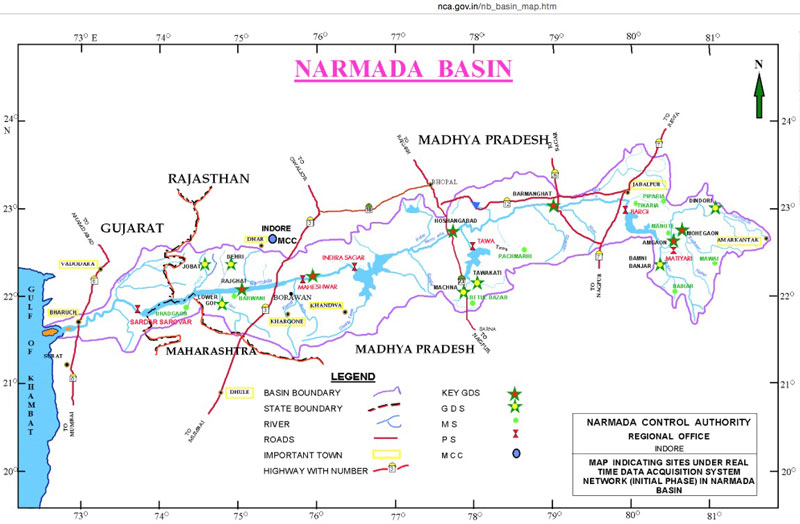
Memories of life in a remote Bhil hamlet on the Narmada river >>
“Those displaced, who are the Scheduled Tribes, belong to the Bhil, Bhilala, Pavra, Tadvi, and Vassawa ethnic groups [of] Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.”
Source: Development and Dispossession in the Narmada Valley >>
Find up-to-date information provided by, for and about Indian authors, researchers, officials, and educators
List of web portals covered by the present Custom search engine
Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the Environment (ATREE) – www.atree.org
Freedom United – www.freedomunited.org
Government of India (all websites ending on “.gov.in”)
Kalpavriksh Environmental Action Group – https://kalpavriksh.org
Shodhganga (a reservoir of Indian theses) – https://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in
Survival International – www.survivalinternational.org
UCLA Digital Library – https://digital.library.ucla.edu
Unesco – https://en.unesco.org
Unesco digital library – https://unesdoc.unesco.org
Unicef – www.unicef.org
United Nations – www.un.org/en
Video Volunteers – www.videovolunteers.org
WorldCat (“the world’s largest library catalog, helping you find library materials online”) – https://worldcat.org
To search Indian periodicals, magazines, web portals and other sources safely, click here. To find publishing details for Shodhganga’s PhD search results, click here >>
Search tips
Combine the name of any particular state, language or region with that of any tribal (Adivasi) community.
Add keywords of special interest (music, poetry, dance just as health, sacred grove and biodiversity); learn about the rights of Scheduled Tribes such as the “Forest Rights Act” (FRA); and the United Nations “Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples”, “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”, “women’s rights”, or “children’s right to education”.
Ask a question that includes “tribal” or “Adivasi”, for instance: “Adivasi way of life better?” (or “tribal way of life worse?”)
Specify any particular issue or news item (biodiversity, bonded labour and human trafficking, climate change, ecology, economic development, ethnobotany, ethnomedicine, global warming, hunter-gatherers in a particular region or state, prevention of rural poverty, water access).
For official figures include “scheduled tribe ST” along with a union state or region: e.g. “Chhattisgarh ST community”, “Himalayan tribe”, “Scheduled tribe Tamil Nadu census”, “ST Kerala census”, “Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group Jharkhand”, “PVTG Rajasthan”, “Adivasi ST Kerala”, “Adibasi ST West Bengal” etc.
In case the Google Custom Search window is not displayed here try the following: (1) toggle between “Reader” and regular viewing; (2) in your browser’s Security settings select “Enable JavaScript” | More tips >>
Note: hyperlinks and quotes are meant for fact-checking and information purposes only | Disclaimer >>
Some clarifications on caste-related issues by reputed scholars >>
