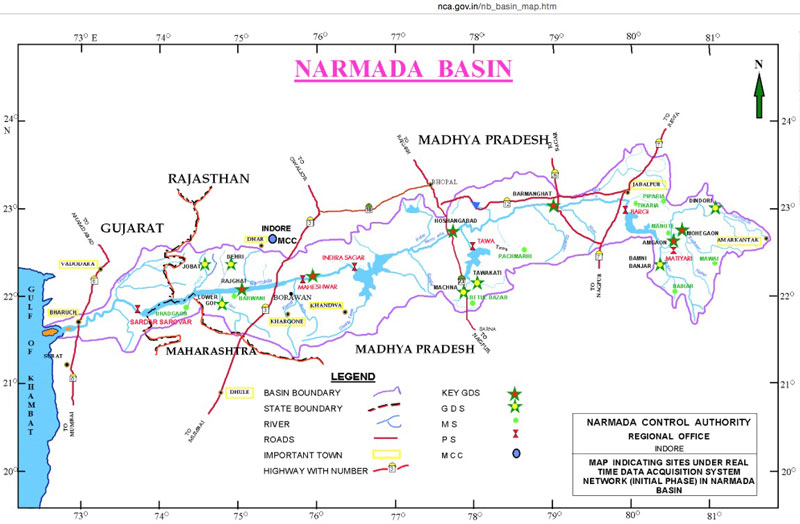
Narmada Parikrama is the circumambulation around holy river Narmada undertaken by its pilgrims. Narmada river is considered to be the lifeline of Central India and is worshipped as Narmada maiyyaor Ma Rewa. The journey covers the route passing from the source of the river, i.e. Amarkantak to the point in Gujarat where it meets the Arabian sea and back. The entire journey covers about 2600 km. Originally the pilgrims completed the tour barefoot, halting in ashrams, temples and local shelters along their way. In modern times, the expedition is also undertaken with the help of vehicles like jeeps, buses and motor-boats. Popular halts along the journey include Ujjain, Maheshwar, Omkareshwar, and Laxmi Narayan Temple in Bhopal.
Source: National List for Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH), Ministry of Culture, Government of India
URL: https://www.indiaculture.nic.in/national-list-intangible-cultural-heritage-ich
Date visited: 25 February 2021
Memories of life in a remote Bhil hamlet on the Narmada river >>
“Those displaced, who are the Scheduled Tribes, belong to the Bhil, Bhilala, Pavra, Tadvi, and Vassawa ethnic groups [of] Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra.”
Source: Development and Dispossession in the Narmada Valley >>
The western region consists of the desert states of Gujarat and Rajasthan as well as Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and western Madhya Pradesh. […] The region is home to a wide variety of people with different religious ‘s and cultures, most of whom have distinctive traditional textiles. They include Jains, Parsis, Hindus and Muslims, as well as tribal groups such as the Bhils and Mina. Yet the dominant characteristic of the traditional saris and odhnis of all these communities, as with all western Indian fabrics, is colour. […] This region’s propensity toward colour has deep roots, for it is here that the Indus Valley civilization developed cotton-growing and -dyeing technologies. – Linda Lynton | Learn more: The Sari: Styles, Patterns, History, Techniques >>
The Bhils of the area [remote tribal villages in northern Maharashtra] practiced their own unique religion, a form of animism and ancestor worship with a heavy dose of magic. But it was clear even at that time that their ancient religious tradition would soon disappear: many Bhils in the area had become devotees of wandering Hindu sadhus and Christian missionaries. Soon, their religious tradition would be looked down by others as ‘primitive’. – Yoginder Sikand | Learn more: “Simple ways of life” (Deccan Herald, 23 December 2012) >>
[Bold typeface added above for emphasis]

“[A] common perception of conversion, prevalent in India, is that all conversions take place only among deprived lower caste or tribal groups, which are considered more susceptible to allurement or coercion. The reality of upper caste conversions is ignored in this climate of cynicism.”– Dr. Ivy Imogene Hansdak in Pandita Ramabai Saraswati: the convert as ‘heretic’ | More about the effects of “casteism” >>
See also
Adverse inclusion | Casteism | Rural poverty
Childhood | Tribal Children’s Right to Education in India
Demographic Status of Scheduled Tribe Population of India (Census figures 2011)
Fact checking | Figures, census and other statistics
Human Rights Commission (posts) | www.nhrc.nic.in (Government of India)
Search tips | Names of tribal communities, regions and states of India
“What is the Forest Rights Act about?” – Campaign for Survival and Dignity
“Who are Scheduled Tribes?” – Government of India (National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, NCST)
Up-to-date reports by Indian journalists and commentators
To search Indian periodicals, magazines, web portals and other sources safely, click here. To find an Indian PhD thesis on a particular tribal community, region and related issues, click here >>
Search tips
Combine the name of any particular state, language or region with that of any tribal (Adivasi) community.
Add keywords of special interest (music, poetry, dance just as health, sacred grove and biodiversity); learn about the rights of Scheduled Tribes such as the “Forest Rights Act” (FRA); and the United Nations “Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples”, “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”, “women’s rights”, or “children’s right to education”.
Ask a question that includes “tribal” or “Adivasi”, for instance: “Adivasi way of life better?” (or “tribal way of life worse?”)
Specify any particular issue or news item (biodiversity, bonded labour and human trafficking, climate change, ecology, economic development, ethnobotany, ethnomedicine, global warming, hunter-gatherers in a particular region or state, prevention of rural poverty, water access).
For official figures include “scheduled tribe ST” along with a union state or region: e.g. “Chhattisgarh ST community”, “Himalayan tribe”, “Scheduled tribe Tamil Nadu census”, “ST Kerala census”, “Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group Jharkhand”, “PVTG Rajasthan”, “Adivasi ST Kerala”, “Adibasi ST West Bengal” etc.
In case the Google Custom Search window is not displayed here try the following: (1) toggle between “Reader” and regular viewing; (2) in your browser’s Security settings select “Enable JavaScript” | More tips >>
Note: hyperlinks and quotes are meant for fact-checking and information purposes only | Disclaimer >>