
Ādivāsi [ādibāsi] may be used in accordance with local conventions; and increasingly so for official purposes (e.g. in “Conserving Tradition and Practices of Adivasi Communities in India” published on NIDM.gov.in); Dr. Ivy Hansdak clarifies:
“Adivasi – which is derived from Sanskrit – is applied to the dark-skinned or Austro-Asiatic indigenous groups of India (usually those from Eastern India). It is a commonly-used term in Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal and Odisha. It is also used by the local Mongoloid tribes of North Eastern India for the migrant workers who were brought in as indentured labourers to work in tea plantations during the colonial period. ‘Tribal’ is a very broad term in the English language and includes all the different indigenous groups of India. The terms ‘indigenous’ and ‘aboriginal’ are not used often as the government claims most groups are indigenous in India. ‘Denotified Tribes’ is only used for those nomadic tribes who were notified as ‘criminal tribes’ during the British Raj [colonial rule]; later they were ‘denotified’ but still bear the stigma.” (emails dated 2020 & 2023)
Minority Rights Group International
Adivasis have distinct languages, religions and forms of self-government, together with a deep bond to their land and respect for nature. […]
The Adivasis of India, written by activists on Adivasi issues, provides a full, yet accessible, historical and legal context to the Adivasis’ claims and to the Indian state’s policy developments towards Adivasis. Both are analysed and their practical implementation discussed. The Report is illustrated with several maps and tables.
The Adivasis of India concludes with a call for an end to state violence and discrimination, and for a recognition and granting of the Adivasis’ rights. This is backed by a set of recommendations which could help protect Adivasis’ human rights and promote peaceful coexistence, meaningful development and equality for all.
Source: The Adivasis of India, Minority Rights Group International (London 1998)
URL: https://www.academia.edu/22238240/The_Adivasis_of_India?auto=download
Date visited: 14 October 2020
For recent developments and up-to-date figures, refer to the “India” country page here: https://peoplesunderthreat.org/countries/india/ >>
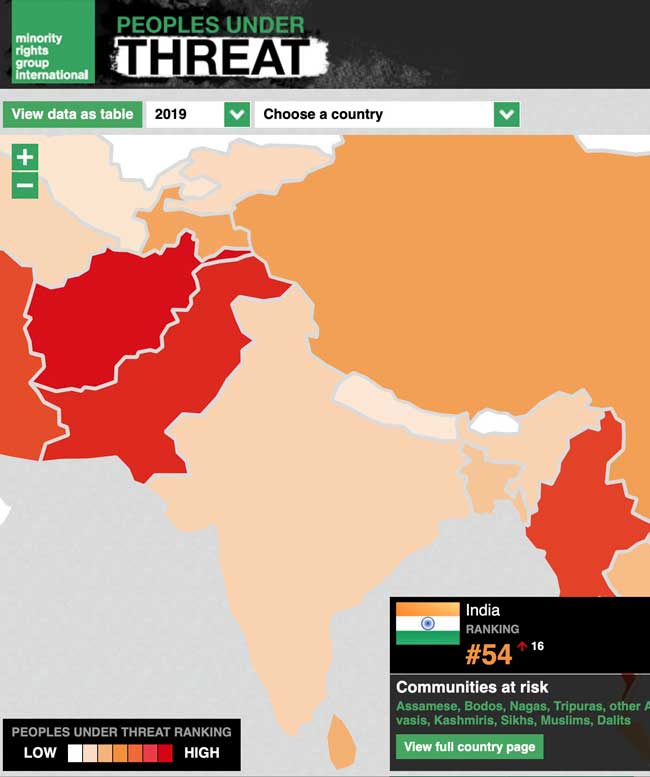
For updates and interactive map, click here >>
Communities at risk
Assamese, Bodos, Nagas, Tripuras, other Adivasis, Kashmiris, Sikhs, Muslims, Dalits
Summary
India ranked 54th in 2019’s Peoples under Threat index and rose 16 places from 2018’s ranking. […]
Source: Minority Rights Group International
URL: https://peoplesunderthreat.org/countries/india/
Date visited: 22 February 2020
Reports in the Indian press | List of periodicals included in this search >>
Search tips
Combine the name of any particular state, language or region with that of any tribal (Adivasi) community.
Add keywords of special interest (music, poetry, dance just as health, sacred grove and biodiversity); learn about the rights of Scheduled Tribes such as the “Forest Rights Act” (FRA); and the United Nations “Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples”, “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”, “women’s rights”, or “children’s right to education”.
Specify any other issue or news item you want to learn more about (biodiversity, bonded labour and human trafficking, climate change, ecology, economic development, ethnobotany, ethnomedicine, global warming, hunter-gatherers in a particular region or state, prevention of rural poverty, water access).
For official figures include “scheduled tribe ST” along with a union state or region: e.g. “Chhattisgarh ST community”, “Himalayan tribe”, “Scheduled tribe Tamil Nadu census”, “ST Kerala census”, “Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group Jharkhand”, “PVTG Rajasthan”, “Adivasi ST Kerala”, “Adibasi ST West Bengal” etc.
In case the Google Custom Search window is not displayed here try the following: (1) toggle between “Reader” and regular viewing; (2) in your browser’s Security settings select “Enable JavaScript” | More tips >>
Note: hyperlinks and quotes are meant for fact-checking and information purposes only | Disclaimer >>
Research the above issues with the help of Shodhganga: A reservoir of theses from universities all over India, made available under Open Access >>
Tips for using interactive maps
Toggle to normal view (from reader view) should the interactive map not be displayed by your tablet, smartphone or pc browser
For details and hyperlinks click on the rectangular button (left on the map’s header)
Scroll and click on one of the markers for information of special interest
Explore India’s tribal cultural heritage with the help of another interactive map >>
See also
Adverse inclusion | Casteism | Rural poverty
Demographic Status of Scheduled Tribe Population of India (Census figures 2011)
Fact checking | Figures, census and other statistics
Human Rights Commission (posts) | www.nhrc.nic.in (Government of India)
Search tips | Names of tribal communities, regions and states of India
“What is the Forest Rights Act about?” – Campaign for Survival and Dignity
“Who are Scheduled Tribes?” – Government of India (National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, NCST)

Tribal Literature by G.N. Devy >>
Free eBooks & Magazine: Adivasi literature and languages >>
“India, a union of states, is a Sovereign, Secular, Democratic Republic with a Parliamentary system of Government. The President is the constitutional head of Executive of the Union. In the states, the Governor, as the representative of the President, is the head of Executive. The system of government in states closely resembles that of the Union. There are 28 states and 8 Union territories in the country. Union Territories are administered by the President through an Administrator appointed by him/her. From the largest to the smallest, each State/UT of India has a unique demography, history and culture, dress, festivals, language etc. This section introduces you to the various States/UTs in the Country and urges you to explore their magnificent uniqueness…” – KnowIndia (Government), States and Union Territories (Visited: 2 September 2023)
Learn more about India’s 28 States and 8 Union Territories – From Andhra Pradesh to West Bengal | Nutrition >>